Or, IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and On-Premises - explained with examples, usage scenario, and consumer details
Or, what are the various differences between On-Premises, IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
Or, what are the definitions of parameters used in the shared responsibility model in the cloud?
Or, Explain IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and On-Premises models with Examples, Target Consumers, and Usage & Purposes.
Descriptions: In this article we will be learning about differences, use cases, responsibilities, and various others about the different cloud models offerings (e.g. IaaS, SaaS, PaaS), including the bonus learning about understanding how On-Premises infrastructure is different than these cloud offerings.
Lets begin with the full forms (as given below):
IaaS: Infrastructure as a Services
PaaS: Platform as a Service
SaaS: Software as a Service
Comparison based on responsibilities (Shared Responsibility Model)
Brief about the parameters used in the comparison table:
Applications: Applications are used by end users. An application can be simply a web browser, a media player, or a program designed to perform some specific tasks.
Data: Data is collection of information in the form of files, media, software etc. The most common data used by users are in the form of pdf files, documents files, images, videos etc…
Runtime: When a program is in running or executing state, this state of the computer is known as Runtime. When you open or execute a program, the Runtime starts, and when you close the program, the Runtime ends.
Middleware: A middleware is software which exists between an operating system and the application running on the operating system. All the middleware software performs communication functions between operating systems and applications running on it.
Database middleware, applications middleware, web-based middleware, and message-based middleware are some most commonly knows middleware software.
OS (Operating Systems): An operating system is system software that manages the computer’s hardware (e.g. CPU, Input/Output Devices, Memory, Ethernets etc…). Most commonly knows operating systems are, Windows, Linux, and Mac.
Virtualization: One of the most commonly used technology now a days which is playing a vital role in cloud computing environment too. Virtualization usage software to simulate the functionalities of hardware which helps running multiple type of operating systems virtually on the single hypervisor operating systems.
Most commonly used virtualization platforms/technologies are VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Citrix Hypervisors.
Virtualization is not limited to just hardware as it also support many verities of applications virtualizations.
Servers: A server is combination of computer hardware and software that provides accessibility of services, over the network connection with the help of applications or in-build roles, to the end users. Most commonly servers are database servers, file servers, front-end servers, web servers etc…
Storage: Almost all the applications produces data that is processed when needed, and stored for further reference and processing. The storage systems are capable of storing any type of data in various forms such as simple block storage, SAN, NAS, Files, Disks, Database tables etc..
Networking: Networking is one of the most critical pillar of cloud or on-premises infrastructure. Without networking, we can’t imagine this whole system to work collaboratively by being tightly integrated with each other. Networking helps two or more applications or servers to talk to each other and share the information or data to serve the users requests.
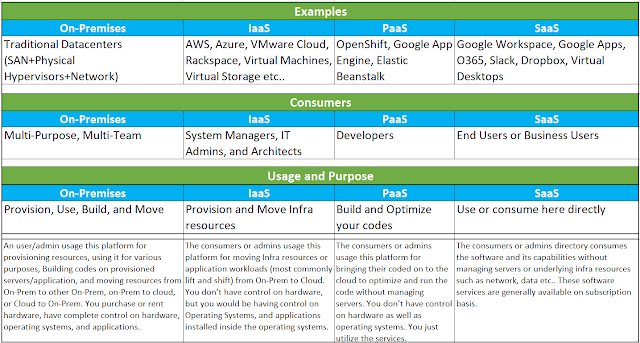
Examples, Target Consumers, and Use Cases / Purposes:
Cheers! Write me back if you have queries or feedback!